IMAC Editor
To start IMAC Editor, open web browser (Google Chrome is recommended for IMAC) and type imac:5000 in the browser address bar.
IMAC Editor contains five areas:
- Main Menu
- Tabs of sequences
- Palette of blocks
- Visual Programming Workspace
- Control panel
- Terminal
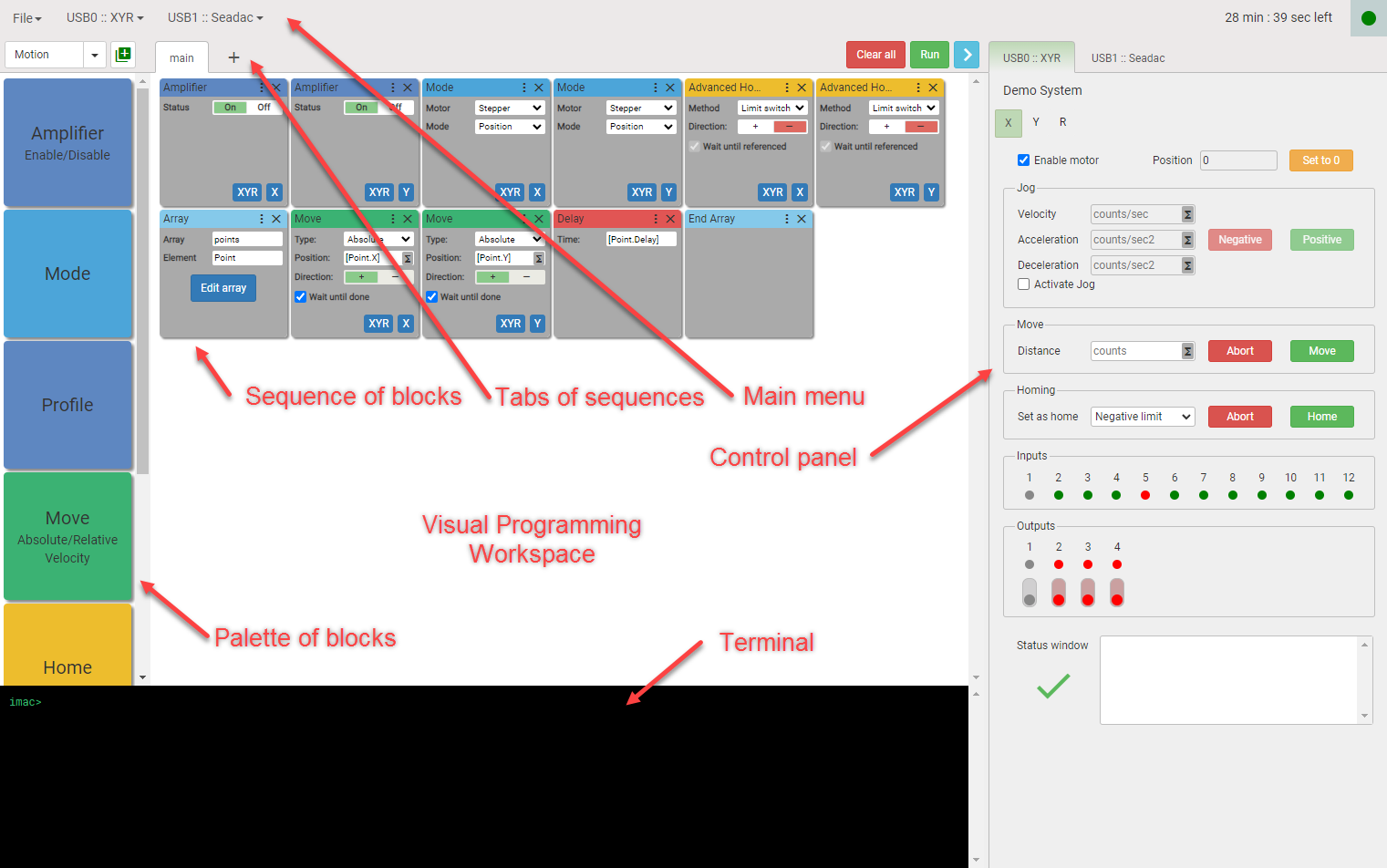
Main menu
Main menu contains File drop-down menu and drop-down menus for each device connected to IMAC.
Manage IMAC program files
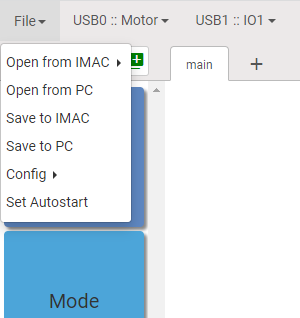
IMAC editor has two options available for opening or saving IMAC programs:
1. Using IMAC’s file system
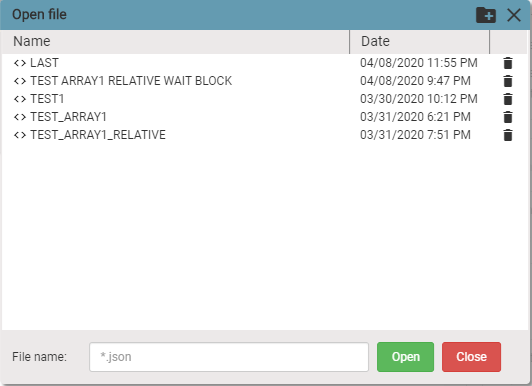
Click on Open from IMAC and the following dialog box appears. Select file and click Open button. Blocks saved in that file will be loaded into visual programming workspace.
Click on Save to IMAC, give a file a name, click Save button and blocks that are displayed on the visual programming workspace will be stored in the file.
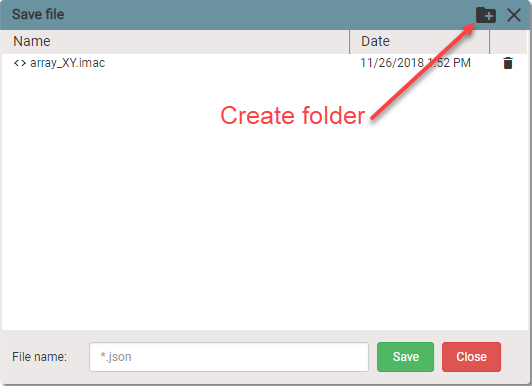
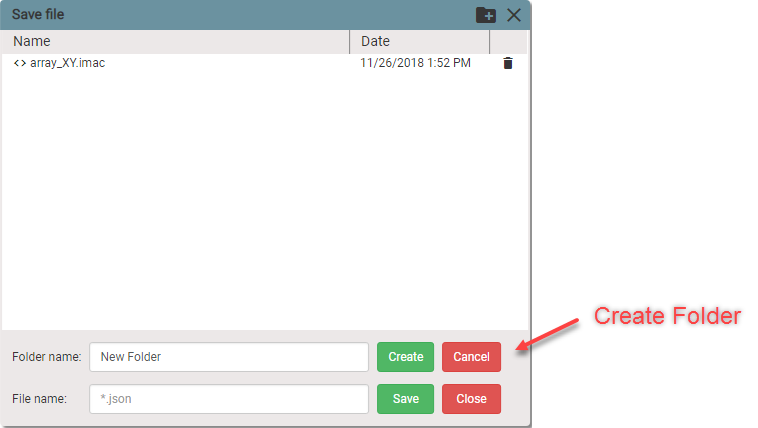
Organize your files by creating folders. Click Create folder icon and additional form will appear.
2. Using User's PC file system or local network shared resource
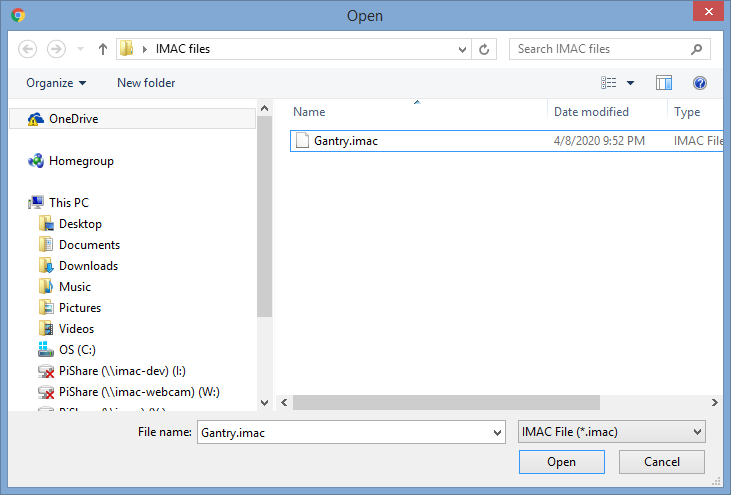
Click on Open from PC and the standard Windows File Explorer dialog box appears. Select file and click Open button. Blocks saved in that file will be loaded into visual programming workspace.
Click on Save to PC. Give a file a name, click Save button and blocks that are displayed on the visual programming workspace will be stored in the file.
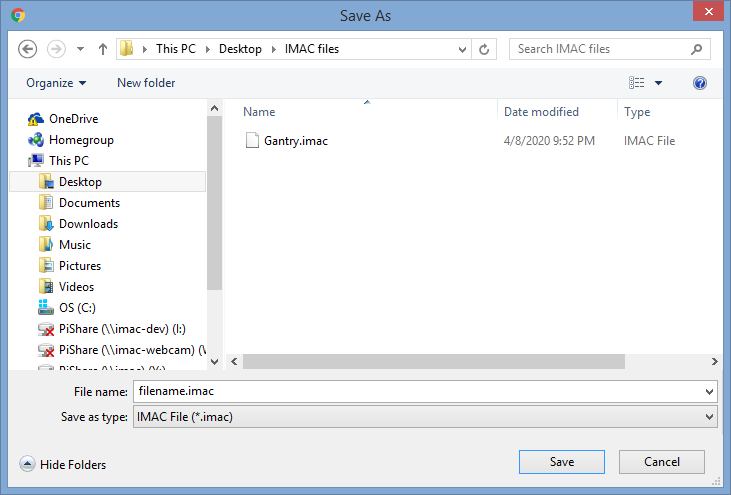
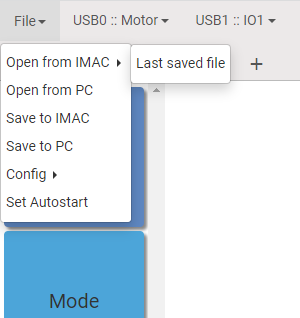
If you nead to open last saved file then click on Last saved file.

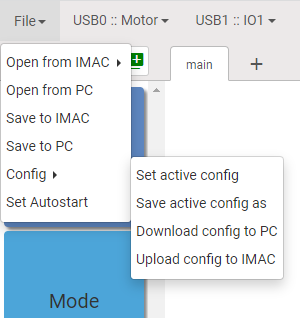
Manage IMAC config files
IMAC allows to save device settings into config files for later use.

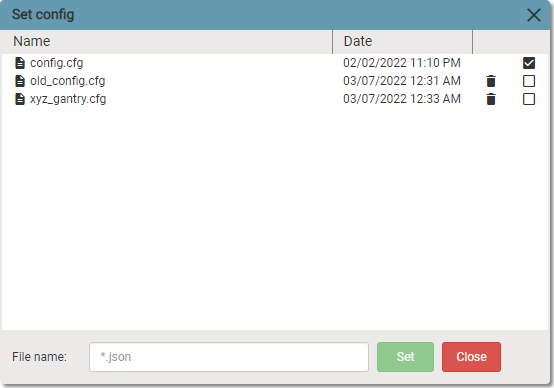
You can select a config file for the current session by clicking on Set active config. The following dialog window will be opened. Select config file and click on Set button.
If you need to make changes to device settings, but you want to keep previous settings, then you need to create a new config file. Click on Save active config as to save current settings into new file. The following dialog window will be open.
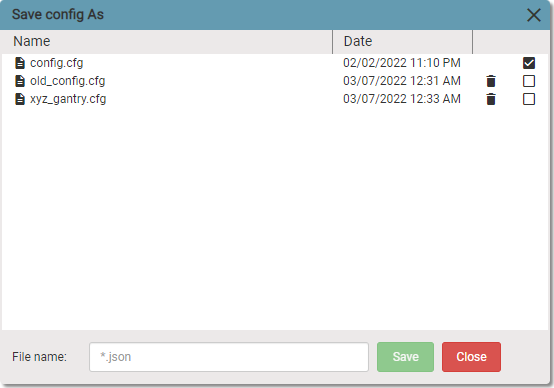
Enter a config file name with .cfg extension and click Save button. You need to select a new file as active config file. Click on Set active config and select new config file.
All changes to device settings are being automatically saved into active config file.
IMAC allows to download or upload config files from user's computer.
If you need to send config file to someone, click on Download config to PC, select file and click Download button.
If you need to use config file you received from someone, click on Upload config from PC, select file and save it. After that you can set uploaded file as active config.
Tabs of Sequences
IMAC programs can consist of multiple sequences. Main sequence is where the program starts. Additional sequences can be added and used as ordinary functions or event handlers. Additional sequences are invokable from main sequence or another additional sequences.
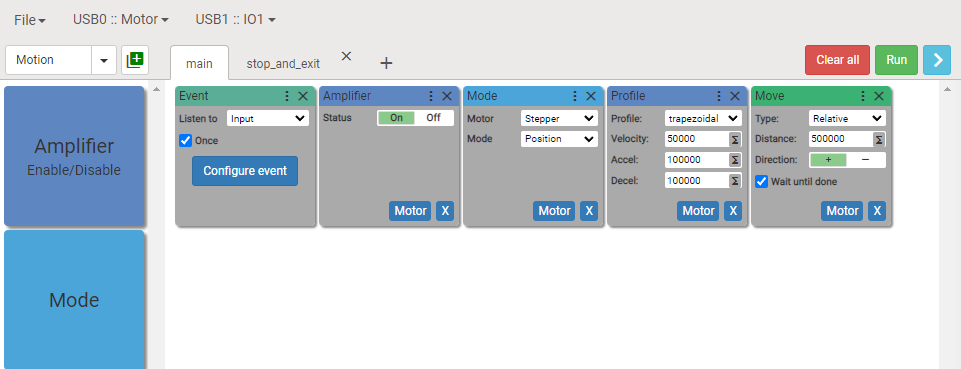
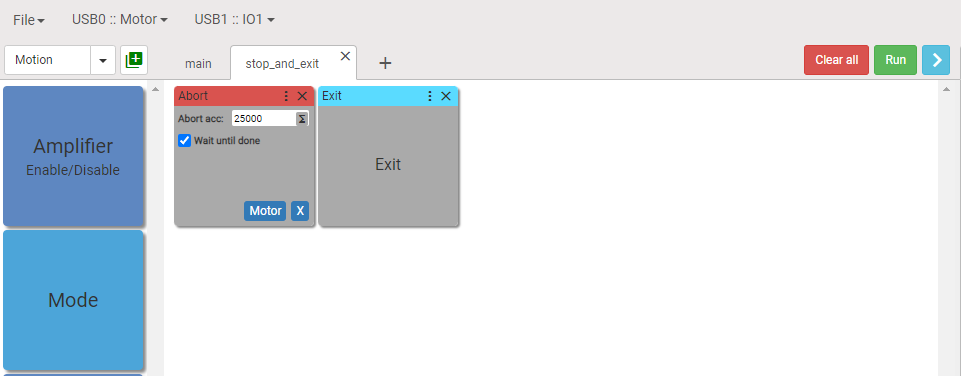
How to use additional sequence as event handler
Blocks
Here is an example of block:
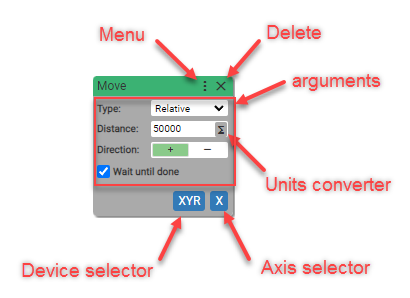
Block palette contains the following command block categories:
- Motion Blocks
- Time / Event Blocks
- I/O Blocks
- Control Flow Blocks
- Math Blocks
- Variable Blocks
- Mics. Blocks
- User Blocks
Motion Blocks
1. Mode
Sets the type of the motor and the mode in which motor works.

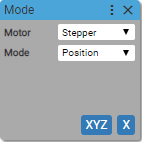
Motor type:
- Stepper
- Servo
Operating mode:
- Position
Sets the motor type to Stepper and operating mode to Position for axis X on device XYZ.
2. Profile
Sets motion characteristics.

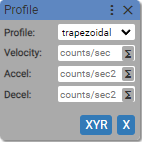
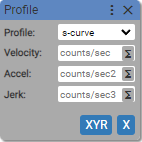
Profile:
- trapezoidal
- s-curve
Velocity: (units: counts/sec)
- positive integer
- [variable]
Acceleration: (units: counts/sec2)
- positive integer
- [variable]
Deceleration: (units: counts/sec2)
- positive integer
- [variable]
Jerk: (units: counts/sec3)
- positive integer
- [variable]
- Sets the motion profile to
trapezoidal, velocity, acceleration, deaceleration for axisXon deviceXYR. - Sets the motion profile to
s-curve, velocity, acceleration, jerk for axisXon deviceXYR.
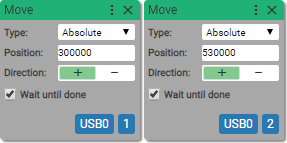
3. Move
Execute motion with specified parameters

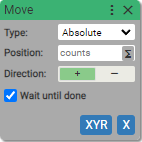
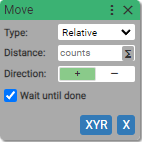
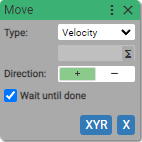
If Wait until done is checked block becomes async.
Type:
-
Absolute
Use when you need to move the axis relative to current homing position.
-
Relative
Use when you need to move the axis relative to current position.
-
Velocity
Use when you need to move the axis at a constant velocity in the selected direction.
Position: (units: counts)
- positive or negative integer
- [variable]
Distance: (units: counts)
- positive or negative integer
- [variable]
Direction:
- Positive
- Negative
Multiplies the value of position or distance by
1if Positive, and-1if Negative.
Wait until done:
- True (checked)
- False (unchecked)
Sets the type and direction of the motion. By default the checkbox Wait until done is checked and that means that next block in the sequence is not being executed until the current motion is completed.
If absolute motion is selected, axis moves to absolute position in counts.
If relative motion is selected, axis moves given counts.
If velocity motion is selected, axis moves infinitely in the selected direction.
Sets motion for axis X on device XYZ.
4. Home
Execute pre-configured (default) home positioning.

Async block
Executes home positioning method that is configured in device settings for axis X on device XYR
5. Advanced Homing
Executes home positioning with specified parameters

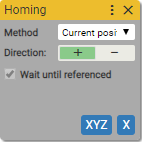
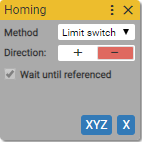
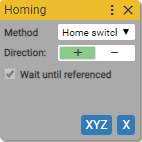
Async block
Method:
-
Current position
Use when the currect position is needed to be set as homing position.
-
Limit switch
Use when one of limits is needed to be set as homing position.
-
Home switch
Use when home switch is needed to be set as homing position.
Direction:
-
Positive
-
Negative
Selects limit switch which axis moves into to set up homing position
Indicates direction which axis moves in to find home switch
Disabled when
Current positionis selected
Wait until referenced:
- True
Always true. Waits for axis completes the homing positioning.
Sets homing method and direction for axis X on device XYZ. Always waits until referenced.
6. Abort motion
Aborts motion

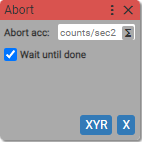
If Wait until done is checked block becomes async.
Abort deceleration: (units: counts/sec2)
- positive integer
Wait until done:
-
True (checked)
-
False (unchecked)
Waits for motion completion if checked.
Aborts motion at axis X on device XYR. Motion gets slower with provided deceleration. Waits until axis stopped if Wait until done is checked.
Time / Event Blocks
7. Wait for digital input
Waits for condition on selected digital input.

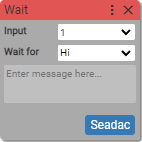
Async block
Input: (units: positive integer)
- number of input
- [variable]
Wait for: (units: Hi / Lo or 1 / 0)
- input state
- [variable]
Waits for Hi condition on input 1 on device Seadac. The next block in the sequence will be executed only if expected condition comes on given input.
8. Listen to event
Listens to events.

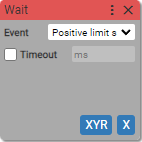
Async block
Event:
- Positive limit switch
- Negative limit switch
Timeout:
- True (checked)
- False (unchecked)
Milliseconds: (units: milliseconds)
- positive integer
Awaits the Positive limit switch is triggered at the axis X on device XYR. The next block in the sequence will be executed only if awaited event happens.
If during the specified time the event is not occurred, the error will be thrown and the further processing of the sequence of blocks will be stopped.
9. Delay
Waits for specified milliseconds.

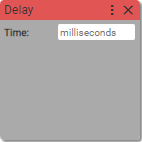
Async block
Time: (units: milliseconds)
- positive number
Waits for the specified time. The next block in the sequence will be executed only after the time is expired.
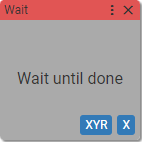
10. Wait until done
Waits until the motion launched by previous block is completed.

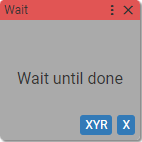
Async block
Waits until axis X on device XYR completes its motion.
Checks the motion at axis X on device XYR. If the motion does not exist (or the motion is ended) the next block in the sequence will be allowed to run.
Example:
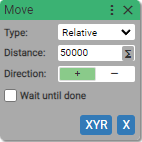
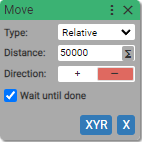
11. Event Listener
Listens to event and executes event handler.

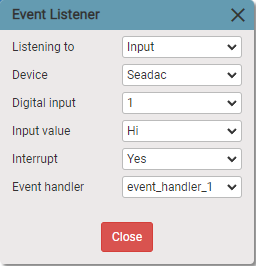
Listen to:
- Input
Device:
- I/O device
Digital input:
- number of input
Input value:
- Hi
- Lo
Interrupt:
- True
- False
Event handler:
- Tab
Once:
- True
- False
Says to interpreter to listen to event in background. As soon as event happens interpreter executes event handler.
If interrupt option is set to true, interpreter does not wait for any async blocks end to execute event handler.
If interrupt is set to false, interpreter waits for async blocks end (like motion completion, awaiting input state change etc.).
If once option is set to true, event listener is being unregistered (removed). It means event handler is being executed only once.
If once option is set to false and if event happens multiple times during execution of event handler or during awaiting async action , event handlers are piled up in the queue. It means event handlers are being executed multiple times, one after another.
When event happens interpreter memorized a block before executing event handler, and when there is no event handlers left in the queue interpreter returns to this memorized block and execute next block after it.
I/O Blocks
12. Set digital output
Sets state of digital output.

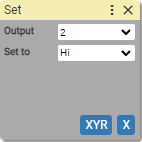
Output: (units: positive integer)
- number of output
- [variable]
Set to: (units: Hi / Lo or 1 / 0)
- output state
- [variable]
When output is set to Hi output transistor is open, conducting current to the load.
When output is set Lo output transistor is closed, no current flows to the load.
13. Read digital input
Reads state of input.

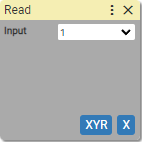
Input: (units: positive integer)
- number of input
- [variable]
Reads value of specified input and saves this value in the program's internal memory. The value can be used in the IF-ELSE statement. Also the value can be assigned to variable name.
Control Flow Blocks
14. Repeat
Opens the beginning of the repeated part of the sequence of blocks.

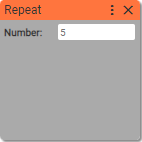
Number: (units: positive integer)
- number of repeats
Defines how many times blocks will be repeated.
Says to IMAC interpreter that starting from the next block there is a chain of blocks ended with End Repeat that should be repeated Number times.
15. End Repeat
Defines the end of the repeated part of the sequence of blocks.

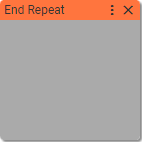
Says to IMAC interpreter that here is the end of a chain of blocks started with Repeat block.
16. While
Opens the beginning of the repeated part of the sequence of blocks. Repeats are conditional and executed if boolean expression evaluated to true.

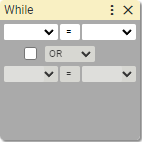
First boolean expression:
first operand:
- Number
- [variable]
operator:
- Equal to
=- Not equal to
≠- Greater than
>- Greater than or equal to
≥- Less than
<- Less than or equal to
≤second operand:
- Number
- [variable]
Boolean operator:
- OR
- AND
Second boolean expression:
first operand:
- Number
- [variable]
operator:
- Equal to
=- Not equal to
≠- Greater than
>- Greater than or equal to
≥- Less than
<- Less than or equal to
≤second operand:
- Number
- [variable]
Says to IMAC interpreter that starting from the next blocks there is a chain of blocks ended with End While that should be repeated if boolean expression evaluates to true.
17. End While
Defines the end of the repeated part of the sequence of blocks.

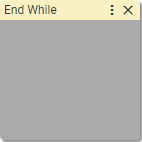
Says to IMAC interpreter that here is the end of a chain of blocks started with While block.
18. If and Else If
Allows for conditional execution of block sequence fragment.

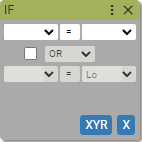

First boolean expression:
first operand:
- Number
- Numner of input
- [variable]
operator:
- Equal to
=- Not equal to
≠- Greater than
>- Greater than or equal to
≥- Less than
<- Less than or equal to
≤second operand:
- Number
- Lo / Hi
- [variable]
Boolean operator:
- OR
- AND
Second boolean expression:
first operand:
- Number
- Number of input
- [variable]
operator:
- Equal to
=- Not equal to
≠- Greater than
>- Greater than or equal to
≥- Less than
<- Less than or equal to
≤second operand:
- Number
- Lo / Hi
- [variable]
If the boolean expression returns true the next blocks are being executed until IMAC interpreter meets next Else If block or associated Esle block or End If block. If the condiction is false the next blocks are being skipped and IMAC interpreter will look for next Else If block or assocciated Else block or End If block to continue execution of the blocks.
Sample use case
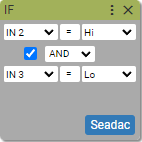
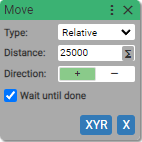
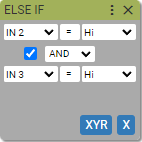
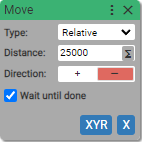

If Input 2 is High and Input 3 is Low then move axis X 25000 counts in positive direction, else if Input 2 is High and Input 3 is Low then move axis X 25000 counts in negative direction, else home axis X.
19. Else


Says to the interpreter to start the execution of the blocks from here to the next End If block if the boolean conditions of associated If of Else If blocks are false.
20. End If


Says to the interpreter that this is the end of If or If-Else statement.
21. Pause

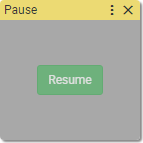
Async block
Says to the interpreter to pause the execution of blocks until the Resume button is clicked.
22. Exit

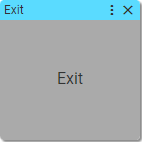
Says to the interpreter to stop execution of blocks and exit.
Math Blocks
23. Basic math
Performs four basic mathematical operations: addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.

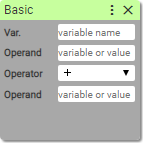
Var.: (string)
- variable name
Operand 1:
- Number
- [variable]
Operator:
- +
- −
- ÷
- ×
Operand 2:
- Number
- [variable]
Saves result of operation into the variable with specified name.
Variable Blocks
24. Value to Variable
Assigns value to the variable.

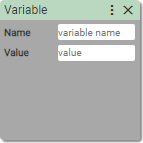
Name:
- string without special characters
Value:
- Number
Creates a variable in the local variable scope and assigns value to it.
25. Varibale to Variable
Assigns variable to another variable.

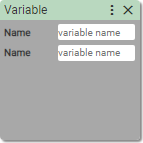
Name:
- string without special characters
Name:
- variable name
Creates a variable in the local variable scope and assigns value of another variable to it. If another variable does not exist in the local scope, it is being looking for in the outer scopes and global scope. If it does not exist then error is being thrown.
26. Parameter to Variable
Assigns value of input / output / register to the variable.

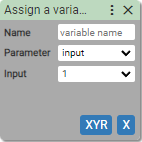
Name:
- string without special characters
Parameter:
- Number of input
- Number of output
- Register address (for motor controller only)
Creates a variable in the local variable scope. Requests value of parameter from device and assings it to variable. If it's unable to receive value of parameter, throws error.
27. Array
Creates an array of elements (ex. points) and executes following blocks once for each array element.

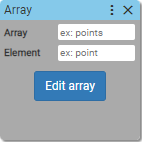
Array:
- string without special characters (name of array)
Element:
- string without special characters (name of array element)
Elements:
- Array
Ways to create array:
- Manually using
add rowandadd columnbuttons. - Importing from csv file.
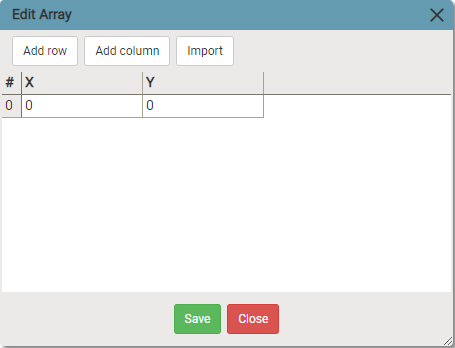
- Using Array Wizard to create csv file and then importing it. Main menu -> Tools -> Array wizard
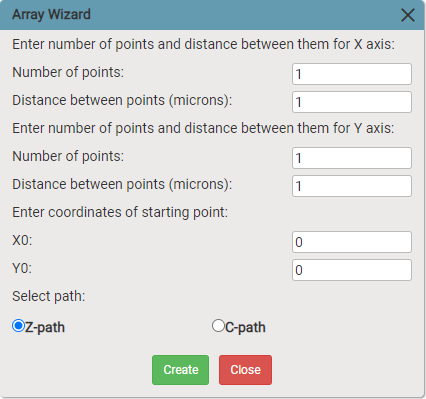
Says to interpreter to execute following blocks once for each array element.
28. End Array
Indicates the end of sequence of blocks executed by array block.

Indicates the end of sequence of blocks executed by array block.
Mics. Blocks
29. Print
Outputs a message to the terminal.

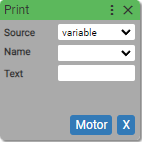
Source:
- variable
- input
- ouput
- register
Name/Input/Output/Register:
- Variable name
- Number of input
- Number of output
- Register address (for motor controller only)
Text:
- string
Outputs a message to the terminal. Message can consist a text with a value of variable/input/output/register.
30. Comment
Adds comment to the block sequence. User adds comments by clicking on the icon inside the block.

Does nothing
User Blocks
The User blocks are the blocks created by user from standard blocks or/and another user blocks. The User blocks can be deep nested. User can create user blocks from another user blocks which consist another user blocks.
Here is created user block which moves the gantry system to the reference point.
To see the inner blocks and edit them click Unfold in the dropdown menu.
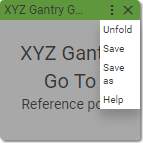
To fold the user block back click Fold.
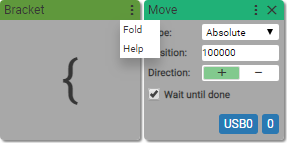
To learn more about User blocks please see The User Block Guide.
Sending ASCII commands through the terminal
User has a full control over the motor drives through the Terminal. Refer to the ASCII Programmer’s Guide for available commands and syntax. The syntax of IMAC ASCII message is:
[usb port]:[axis letter][command code][command parameters]
Examples:
usb0: 1 g r0x70
Get the value of register 0x70 at axis 1 of motor drive connected to USB port 0.
usb0: 0 s r0xc8 0
Set the trajectory generator to absolute move, trapezoidal profile
usb0: t 2
Execute homing.